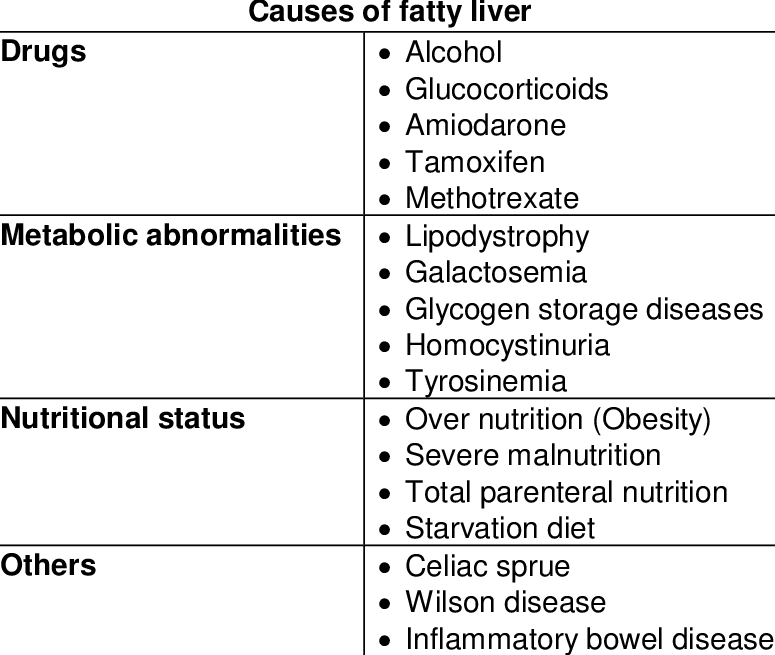
Nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases (NAFLDs) are common, affecting about a third of the population
They affect about seven million Americans. These diseases usually develop when there is a genetic predisposition to it, but can also be acquired through environmental factors such as excessive alcohol intake.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver is more commonly known as NAFLD. This is an umbrella term that covers alcoholic fatty liver and nonalcoholic fatty liver. This type of liver disease is usually characterized by abnormal liver tissue. The liver has become unable to properly metabolize and process substances. When your body is unable to properly process and utilize these substances, it is referred to as a fat accumulation in the liver. In nonalcoholic fatty liver, this accumulation is primarily caused by a diet with excess amounts of alcohol and a lifestyle where obesity and poor nutrition are commonplace.
Nonalcoholic steatosis is a mild form of nonalcoholic fatty liver. This kind is most common in people who are obese or have been inactive for quite some time. Your liver is functioning fine when your body is in good condition. However, this condition results when your body is unable to efficiently absorb and use glucose and sugar. When it's this severe, it can even lead to the growth of cancerous cells in the liver.
Acute nonalcoholic steatosis is a much more serious form of nonalcoholic fatty liver, which occurs suddenly and without warning. This is usually brought on by surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy or liver transplant. It may take several months for symptoms to surface after an acute nonalcoholic fatty liver condition develops. Once they do, though, you will likely find yourself struggling to lose weight because you will be at risk of developing cirrhosis.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver is the second-leading cause of death in the U.S. It accounts for about one-third of all liver cancer cases and about one-half of all liver transplants performed each year. It is the most common cause of heart failure in men. Women are more likely to have gallbladder disease, gallstones and hepatitis, so if you do have any of these conditions, it is especially important to visit your doctor right away.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver is also the leading cause of cirrhosis of the liver in the United States
It is the largest organ in the body and can affect many other parts of the body. People who have NAFLD are at a higher risk of developing heart disease, stroke and certain types of cancers. In addition, having NAFLD increases a person's lifetime risk for osteoporosis and cataracts. It is also more likely that someone with this condition will develop Alzheimer's disease.
NAFLD is not always a life-threatening condition, but it requires treatment. Surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy are the main treatments for people with this condition. Many people do not understand that one operation will not solve the problem, but this is the only sure way to get rid of fatty liver. Surgery alone cannot permanently remove the fatty tissue of the liver; it is very important that the patient follows a healthy, correct diet and exercise program.
Since non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is highly treatable, there is no reason you should live with the effects of fatty liver disease forever. The good news is that non-alcoholic fatty liver disease can often be cured with a healthy, low-fat diet and exercise. You no longer need to suffer from this debilitating condition. Click here cth.co.th to learn more about non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and NAFLD and see if you qualify for help today.